Surgical treatment in severely immunocompromised patient with invasive fungal infection
Kirurško zdravljenje imunokompromitiranega bolnika z invazivno glivično okužbo
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18690/actabiomed.196Keywords:
Aspergillus, surgery, T-cell lymphoma, spontaneous pneumothorax, immunocompromised patientAbstract
Purpose: We present a case report of successful surgical treatment of a 58-year- old severely immunocompromised male patient with invasive fungal infection.
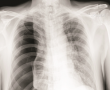
Case presentation: A 58-year-old male with a smoking history of 30 years was admitted to hospital because of sudden shortness of breath. Radiographic imaging showed an extensive pneumothorax. The patient had a history of T-cell lymphoma, B-cell MALT lymphoma, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. He had also previously undergone chemotherapy. During hospitalization, his health state started to deteriorate. On the basis of imaging and microbiological culture results, he was diagnosed to have a fungal infection with Aspergillus fumigatus. After careful preoperative care, preparations, and several consultations, we performed video-assisted thoracic surgery. Because of poor visibility, inaccessibility, and rupture of an intercostal artery, we performed thoracotomy with excision of the right lung apex. Histopathology and microbiology results confirmed the initial diagnosis. Postoperatively, a 1-year treatment regimen with voriconazole was introduced. The follow-up CT scan showed no signs of fungal infection progression. The patient was given further instructions and discharged from the hospital in a cardiorespiratory compensated state.
Conclusion: Despite poor prognostic factors, the surgical procedure was successful and the patient’s health state considerably improved.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2020 Acta Medico-Biotechnica

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.