Alveolar hemorrhage after treatment with combined antiplatelet and anticoagulation therapy before and during primary coronary intervention in acute coronary syndrome with ST elevation: A case report
Alveolarna krvavitev kot zaplet po kombiniranem zdravljenju z antiagregacijskimi in antikoagulantnimi zdravili pri primarni koronarni intervenciji pri bolniku z akutnim koronarnim sindromom z elevacijo ST veznice – prikaz primera
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18690/actabiomed.22Keywords:
hemoptysis, alveolar hemorrhage, myocardial infarction, eptifibatide, primary coronary intervention, antiplatelet therapyAbstract
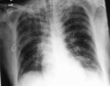
Platelet inhibition with aspirin and systemic anticoagulation with unfractioned heparin to reduce the incidence of recurrent thrombosis after primary coronary intervention (PCI) has been the standard of care for patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) with ST elevation for some time. Eptifibatide is the platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor that is often used. Bleeding complications occur most often at sites of vascular access and are more common in elderly patients. Alveolar hemorrhage with hemoptysis is a rare complication. We describe the case of a 43-year old smoker with an ST elevation myocardial infarction admitted for PCI. He was treated with standard anticoagulation and dual antiplatelet therapy before admission. Hemoptysis began approximately five minutes after the intracoronary application of eptifibatide at the end of the procedure. Supportive care including endotracheal intubation, mechanical ventilation, transfusion of packed red blood cells and reversal of all anticoagulation. Alveolar hemorrhage is life-threatening but adequate intensive supportive measures can be life-saving.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2009 Acta Medico-Biotechnica

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.