Use of Botulinum Toxin for the Treatment of Headache and Facial Pain
Uporaba botulinusnega toksina za zdravljenje glavobolov in bolečin obraza
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18690/actabiomed.288Keywords:
botulinum toxin type A, chronic migraine treatment, pain modulation, clinical pain management, headache disordersAbstract
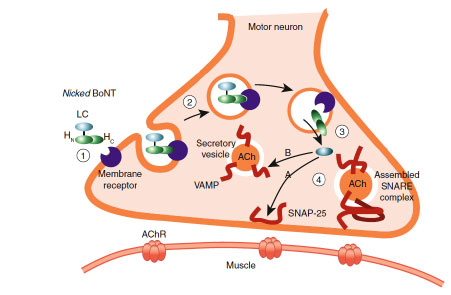
Botulinum toxin (BT) is widely used in cosmetics and clinical practice. This literature review explores the applications of BT for the management of headaches and facial pain. The most widespread, well-reported, and ALIMS and EMA approved application for BT is in preventing chronic migraine at doses between 165–196 IU. After an incidental discovery, BT was validated through several RCTs, including most notably, the PREEMPT study. Following validation, BT was approved for use in treating chronic migraines. According to current guidelines, BT is used for the prevention of chronic migraines in patients who are resistant to other forms of therapy, such as triptans or NSAIDs. The most widely used BT injection protocol was established in the PREEMPT study and recommends 31–39 injection sites. In other primary headaches, such as tension-type headaches, there is little and confounded evidence of the efficacy of BT. However, some small-scale studies reported that BT outperformed placebo and improved pain in trigeminal autonomic headaches. BT is also used to treat chronic facial pain, most notably trigeminal neuralgias, with encouraging results in RCTs. While the primary mechanism of action of BT is the inhibition of acetylcholine release from terminal cholinergic nerves, more specific mechanisms of pain relief are yet to be elucidated, especially for migraine headaches. Our review of relevant published literature indicates that BT therapy is safe, generally well-tolerated and efficacious, and is a viable option for the management of certain primary headaches and chronic facial conditions.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Milena Šibalić, Danka Mostić Stanišić, Dragana Milivojević (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.